
NOSTALGIA
MY GOOD OLD DAYS
AT AIIMS- JOINT ROUNDS WITH NEUROSURGERY DEPARTMENT (1983-1986)
AT THE ANNUAL MEETINGS OF NEUROLOGICAL SOCIETY OF INDIA (Prior to 1990)

THE SYMBIOSIS
1. The ultimate goals are same
2. The anatomical, physiological and pathological substrates are partly same.
3. The methods of clinical assessment, including history taking, physical examination and interpretation of investigation are mostly same.
THE ASSYMITRY and DIFFERENCES
1. Temperamental, philosophical and personality differences.
2. More emphasis and importance of History taking and its interpretation for a neuro-physician.
3. Neurologists can not do surgery but can medically treat many neuro-surgical ailments.
4. Neurosurgeons can treat some neurological conditions, but need training.
5. Hard core neurological conditions to which neurosurgeons are not exposed, are too many, too numerous in community and too complex for them.
MEDICAL CONDITIONS AMENABLE TO SURGERY
Neurosurgeons specializing in surgical treatment of following medical conditions need to be well versed with their medical management also.
- Epilepsy
- Movement Disorders; Stereotactic Functional
- Psycho- surgery: addictions, OCDs
- Chronic intractable pains
- Spasticity
- Peripheral Mono-neuropathies — traumatic and Non-traumatic
HOW THE HISTORY TAKING BY A NEUROLOGIST DIFFERES
While Eliciting history:
- Let patient and then caregiver speak.
- No interruption for at least initial 2 minutes, No irritation
- Make rough notes-in mind or on paper.
- Keep ready Leading Questions in the mind and ask them only when patient has completed
- Think anatomy first
- Think pathology second
- Think etiology third
- Think deficit/handicap fourth
- Family history may be more often positive in neurology
HOW THE PHYSICAL EXAMINATION BY A NEUROLOGIST DIFFERS
- More importance of general Systemic Examination
- Never forget Optic Fundus.
- Higher Mental functions-orientation, memory, executive functions, language, apraxia, agnosia.
- Download on phone-MMSE, Montreal Cognitive scale, NIHSS
- Mental Status- Mood and Affect, Conversion reaction. Functional.
- Movement disorders; Phenomenology, anatomy, rhythmicity, rate, amplitude, effect of rest, posture, kinesis.
- Polyneuropathy
- Myopathy
- Neuro-muscular Junction—fatiguability
STROKE—WARNING SIGNS
CORE MESSAGES ABOUT STROKE (1)
1. Remember the Warning Signs of Stroke, Act upon them, Popularize them, Institutionalize them.
2. First Aid of Stroke, while waiting for transfer: let patient be supine. ECG, base-line Investigations, Don’t treat Blood Pressure CT Scan First. Don’t waste time on MRI in the beginning.
3. If no hemorrhage, load with Aspirin 300 mg +/- Clopidogrel.
4. Urgent transfer to a Stroke ready Hospital [CT scan, MRI, Cath lab, ICU, laboratory, Neurosurgery, Physicians]
5. Chase the Time Windows
Don’t neglect TIAs. : Investigate them like Stroke
TIME WINDOWS
1. For IV Thrombolysis– 3 to 4.5 hours. BUT SOONER THE BETTER
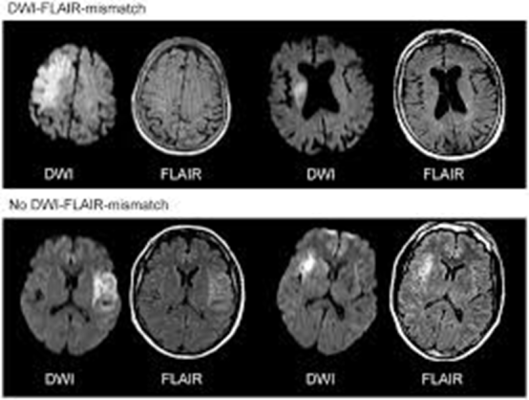
2. If later then 4.5 hours OR Wake-up Stroke- (up to 24 hours)
The Mismatch on MRI Between DWI and Flair can dictate feasibility of Mechanical Thrombectomy in large Vessel stroke.
CORE MESSAGES ABOUT STROKE (2)
6. Beware of Stroke Mimics:
- Seizures
- Migraine
- Fainting
- Infections, such as encephalitis, meningitis, or sepsis
- Toxic-metabolic abnormalities, such as hypoglycemia or hepatic encephalopathy
- Functional neurological disorder (FND)
- Brain tumors
- Space-occupying lesions/ Subdural hematoma
Acute Care Beyond 24 Hours:
- Stroke Unit. Homeostasis.
- Supportive and Symptomatic treatment.
- Judicious use of anti oedema measures
- Surgical decompression in selected cases
Secondary Prevention:
- Investigate and Control the risk factors
- Common: (Hypertension, diabetes, Tobacco, Alcohol, Lipids, Exercise)
- Uncommon: (for young patients with no common risk factors)
Never forget Rehabilitation:
Refer, persuade, follow with Therapists: OT/ PT/ SLT/PSYCHO/
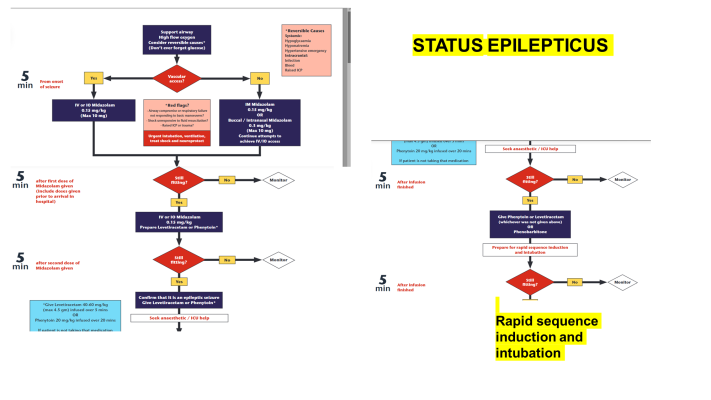
CORE MESSAGES ABOUT EPILEPSY
- First Aid of an epileptic seizure
- Management of Status Epilepticus
- Follow a semiology-based description and classification
- Try to stick to monotherapy while ensuring Gradual titration, monitoring of side effects, Drug levels, compliance.
- Avoid Polytherapy as much as possible.
- For generalized epilepsies Valproate is the drug of choice

CORE MESSAGES ABOUT HEADACHES
Learn by Heart the diagnostic Criteria of common headaches by International Headache Association:
- Migraine
- Tension Type Headache
- Cluster headache.
- Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias (Trigeminal neuralgia)
- Raised Intracranial Pressure.
- Thunderclap headache.
MIGRAINE
Headache characteristics
- The headache has at least two of the following characteristics:
- Unilateral location
- Pulsating quality
- Moderate or severe pain intensity
- Aggravation by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity
Non-headache symptoms
During the headache, the patient has at least one of the following:
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Photophobia and phonophobia
TENSION TYPE HEADACHE
- Frequency: At least 10 episodes in a month for at least 3 months, or at least 15 episodes per month on average for at least 3 months
- Duration: Episodes last 30 minutes to 7 days
- Location: Pain is on both sides of the head
- Quality: Pain is pressing or tightening, not pulsing
- Intensity: Pain is mild or moderate
- Exacerbation: Pain is not made worse by routine physical activity
- Nausea and vomiting: No nausea or vomiting, or no more than one of photophobia or phonophobia
- Other diagnoses: Not better explained by another ICHD-3 diagnosis
CORE MESSAGES ABOUT TREATMENT OF MIGRAINE
Acute Symptomatic Treatment.
- Paracetamol + Metclopromide
- NSAIDs
- Opioids
- Triptans.
Beware of over-use of analgesics
- Not more than 3-5 days in a month
- Side Effects
- Dependance
- Rebound Headaches
Long Term Prophylactic Treatment
- Indicated if severe Headache Frequency more than 4-5 per month.
- Gradually up-titrate the dose.
- Beneficial effects occurs after 2-3 weeks.
- Usually given for 4-6 months.
________________________________
Medicines
- Propranolol 40-120 mg/day
- Amitriptyline 10-25 mg OD at 07 pm
- Topiramate 50-100 mg/day
RED FLAGS FOR PRIMARY HEADACHES
Red flag symptoms indicate a higher risk of a secondary cause for the headache and warrant further investigation
Headache type
A new or worsening headache type, or a thunderclap headache that reaches maximum intensity within 60 seconds
Headache location
A headache that occurs in the middle of the night or first thing in the morning, or a headache that’s worse on one side of the head
Headache triggers
A headache that’s triggered by coughing, sneezing, bending down, or Valsalva maneuvers
Headache duration
A headache that progressively worsens, or a headache that occurs within 5 days of a head injury
Other symptoms
A headache associated with fever, neck stiffness, reduced level of consciousness, vomiting, or loss of vision
Age
A headache that occurs in someone over 50 years old, or a new onset headache in middle age
Signs of systemic illness
A headache associated with signs of systemic illness, such as a rash
Pathological Processes not Commonly Encountered by NEUROSURGEONS
TOXIC, METABOLIC, NUTRITIONAL
EXAMPLES
- Sub Acute Combined degermation of Spinal Cord
- Wernicke Korsakoff Syndrome
- Hepatic / renal Encephalopathy
- Hyponatremia/ electrolytes
- Hypoxic/ ischemic Encephalopathy
- Phenytoin and other medicine overdose
- Substance abuse/poisonings
COMMON CHARACTERISTICS
- Always symmetrical
- Syndromic Constellations
- Not localizable in anatomical terms
- Often other systemic features
Pathological Processes not Commonly Encountered by NEUROSURGEONS (2)
DEMYELINATING AND AUTO-IMMUNE
EXAMPLES
- Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis [ADEM]
- Multiple Sclerosis [MS]
- Neuro-Myelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders
- Auto-immune Encephalitis’s
- Para-neoplastic Syndromes
COMMON CHARACTERISTICS
- Often Symmetrical
- But may also be asymmetrical.
- Monophasic or Multiphasic with relapses and remissions
DEGENERATIVE
EXAMPLES
- Motor neuron Disease
- Parkinsonism
- Alzheimer’s dementia
- Spino-Cerebellar Ataxia
- Myopathies
- Neuropathies
COMMON CHARACTERISTICS
- Pick and Choose specific cells or tracts
- Usually Symmetrical
- Gradual Onset
- Slowly worsening.
- Mostly Untreatable
- Not localizable at a single anatomy
- May be familial
समुद्र तो आपको जाना ही पड़ेगा
Neurology OPD and Wards
“He who studies medicine without books sails an uncharted sea, but he who studies medicine without patients does not go to sea at all. – Sir William Osler
* * *






