
CHALLENGES IN APHASIA REHABILITATION (1)
TREATMENT GAP
a) Awareness and education
b) Lack of Conviction and patience for efficacy of Speech Therapy
c) Paucity of resources –
* Personnel
* Software
* Hardware
d) Missing anguish, desire and demand in the minds of stakeholders
YouTube पर विडियो देखने के लिये यहाँ लिंक पर क्लिक करें https://youtu.be/h_MnD_5hqKA
CHALLENGES IN APHASIA REHABILITATION (2)
THE NATURE OF THE PROBLEM
Difficulties in –
● Diagnosis
● Classification
● Profiling
● Therapeutic Research due to Heterogeneity and Confounding variables
Challenges for a Neurologist
● Post-stroke aphasia persists as a long-term disability in about 25% of survivors (ranging from 21 to 38%).
● A general neurologist often uses non-Standardized and non-validated, ad hoc assessment, in OPD and bedside, though this is not an ideal situation.
● Assessment of aphasia is time and labour intensive, there are no short cuts, yet here are many valuable simple tips for a busy neurologist.
● Computers and smartphones are proving literally handy and very useful in testing aphasia and implementing therapy.
● Aphasia in multi-lingual speakers poses special challenges. It becomes imperative to assess all the languages used by PWA.
● The clinical profile of aphasia may vary in the two or more languages used by PWA.
Rehabilitation
A variety of cares that can help one
*get back or
*keep or
*improve
Abilities that are needed for daily life at
# home,
# work,
# leisure,
# travel and
# hobby
Rehabilitation for Aphasia
To speak in all situations
To Listen and understand
To participate in conversation at social events
To Read
To Write
To do arithmetic
To associated cognitive abilities, Memory, visual-spatial, executive function
To have normal mood/affect (Euthymia)
To have normal familial and social life
Steps in Rehabilitation
● Assessments
● Goal Setting
● Therapies for restoration of lost abilities
● Communication Partner Training
● Aphasia Friendly Social Environment
● Having reached the limits of restoration and even before that
■ Adaptation
■ AAC: Alternative. Augmentative. Assistive devices
● Acceptance, coping
● The new normal
● Eternal Striving
Assessments
○ Severity of aphasia
○ Clinical profile and syndrome
○ Impairment based profile
○ Functional communication profile
○ Other neurological deficits (NIHSS)
○ Other cognitive deficit
○ Quality of life
○ Psycho-social aspects
○ Status of care givers
Clinical Examination for Aphasia
Auditory Comprehension
- Single Words
- Commands, Sentences
- Discourse, paragraphs
Articulation
- Recitation, singing
- Simple words
- Complex Words
- Sentences
Fluency
- Phrase length
- Agrammatism
- Stereotyped utterance
- Word finding difficulty
- Phonological paraphasias
- Semantic paraphasias
- Neologisms
- Circumlocution
Repetition
- Syllable
- Words – high frequency & high imageability
- Words – low frequency,
low imageability
- Phrases
Naming
- Body parts
- Real objects
- Pictures
- Question Based
- Effect of cueing
(phonemic & semantic)
- Rejection of wrong answers
Clinical Examination for Aphasia
Reading
- Matching letters, syllables, words, numerals
- Pointing to letters, syllables, words, numerals
- Reading aloud letters, syllables, words, numerals
- Sorting words & non-words
- Word picture matching
- Word sentence matching
- Filling in the blanks in sentences
- Reading a paragraph and answering questions
Writing
- Copying letters, syllables, numerals, words, sentences
- Writing to dictation – letters, syllables, numerals, words, sentences
- Signature, name, address, automatic sequences
- Written naming of objects, pictures
- Written description of a picture scene
Related higher mental function
Aphasia is not an exclusively language related problem.
- Working memory
- Short term memory/ recent memory
- Remote memory
– Episodic/semantic
– Explicit/ Implicit - Attention, arousal
- Executive functions
- Sensory perception – vision, hearing
- Motor dexterity, skill, apraxia, procedural memory
- Visuospatial function, agnostics.
Aphasia Syndromes are Passe
Syndromic classifications have been helpful as a shorthand summary of a patient’s language disorder.
However, syndromes have lost their theoretical and practical relevance.
Newer classifications based on neurolinguistics and cognitive neuropsychology requires modifications in methods of clinical examination.
We must adopt a deficit-based approach instead of a syndrome-based one.
Functional Communication
Performance of a patient on a diagnostic test battery of aphasia may not have very high correlation with his or her communication in daily life.
Communication involves quick actions of
- Role playing,
- Give and take,
- Pause & participate,
- Listen and respond,
- Gesture & writing.
Psychometrically valid protocols for assessment of functional communication are based on observations of actual interactions.
Quality of Life
- Quality of life ratings have become an important aspects of measurement, which addresses the question of how a person experiences aphasia, how its meaning influences behavior and interactions and includes psychosocial factors such as loneliness, difficulty making friends, lowered self-esteem and depression.
- Quality of life assessments incorporate the individual and caregivers multidimensional and subjective evaluation of their physical, mental, emotional, family and social functioning.
- Stroke specific measures of health related quality of life, which is further fine-turned for use in persons with aphasia, have been developed.
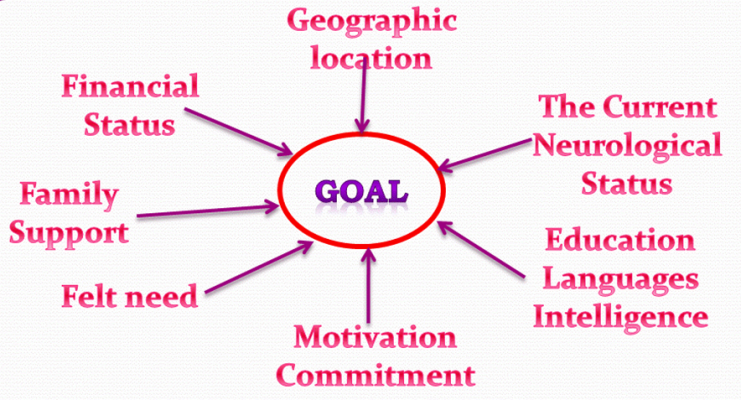
Goal Setting for Rehabilitation
SMART Goals
S – Specific
M – Measurable and meaningful
A – Achievable
R – Realistic
T – Time Bound
Short term
Medium Term
Long Term
BETTER THEORETICAL UNDERSTANDING
- Better theoretical understanding of brain damage and recovery at neurobiological level.
- Potential avenues for repair, replacement, enhancement.
- Pharmacotherapy
- Nerve Growth factors
- Stem cells
- Transcranial Brain Stimulation
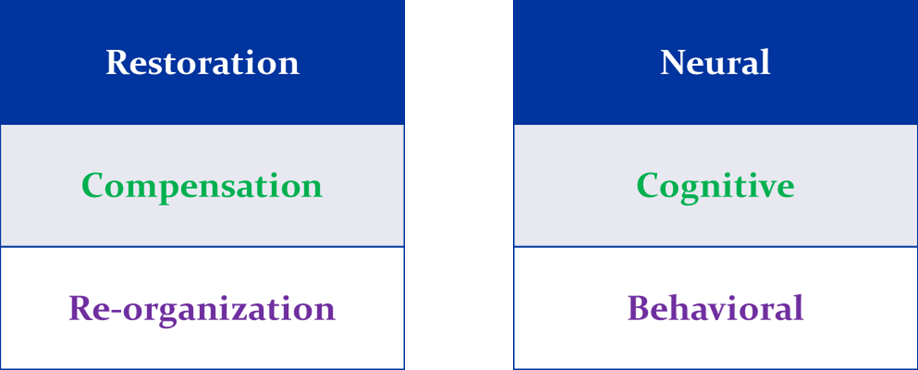
Multilevel Processes in Recovery from Aphasia
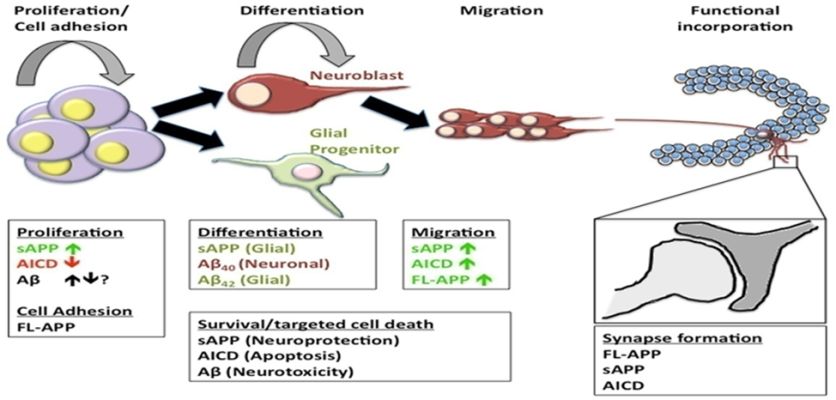
NEUROGENESIS
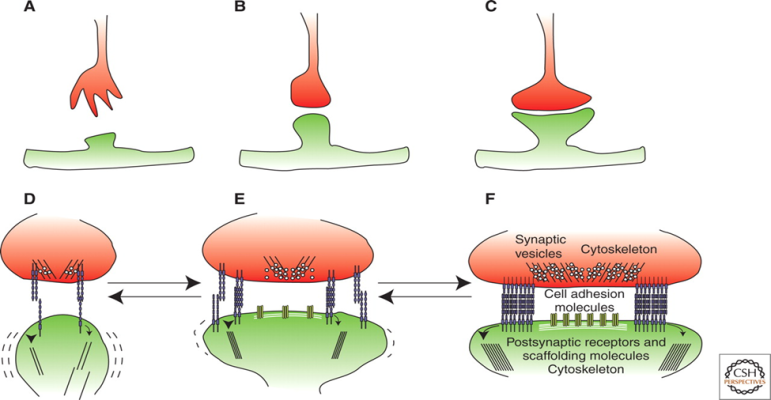
SYNAPTOGENESIS
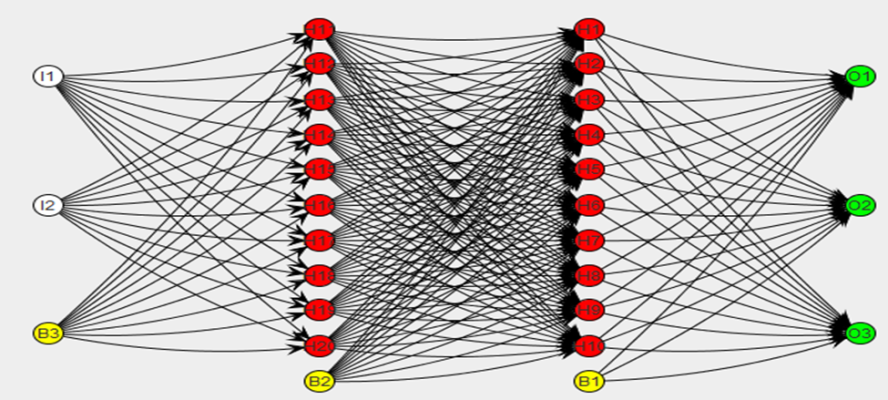
NEURAL NETWORKS
BETTER THEORETICAL UNDERSTAING OF NEUROLIGNUISTICS
COGNITIVE NEUROPSYCHOLOGY OF LANGUAGE FUNCTION
- Better, Standardized, validated tools to assess aphasia.
- Potential theory of Aphasia and theory of aphasia therapy
- Potential new methods of speech therapy

Therapy works
● The mainstay of therapy is behavioral approaches that use language-based drills administered by Speech Language Pathologists [SLPs] through face-to-face interaction between a patient [PWA] and a clinician.
● SLP provides targeted stimulation of selected language tasks and communication skills.
● The recent systemic review suggests that SLT is generally beneficial.
● However, we do not know which treatment approach might work best for a specific patient, something akin to precision treatment.
Types of Therapies
● There is an implicit assumption that SLT-assisted improvement is due to structural and functional neuroplasticity. The latter may be long-lasting or short lasting.
● Approaches to therapy and rehabilitation may be grouped into two broad categories:
● — Impairment-based therapies, which refer to one of the many ‘Cognitive neuropsychological Models of Language’
● — Life Participation Approaches, which emphasise overall functional communication in daily life.
The two approaches are not mutually exclusive or contradictory; in fact, they are complementary to each other.
PHARMACOTHERAPY
Many medicines have been studied in treatment of aphasia.
The results have not been very impressive till now, but prospects are improving.
Pharmacological augmentation of speech therapy may be more robust and reliable with stimulants, cholinesterase inhibitors, dopamine agonists and other medications.
Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation
● Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation [rTMS]
● Transcranial direct current stimulation [tDCS]
● Have been employed in chronic aphasia
● Either to suppress the maladaptive and inhibitory right hemisphere activity
● Or to stimulate compensatory left hemispheric peri-lesion areas.
TRANSCRANIAL MAGNETIC STIMULATION

TRANSCRANIAL MAGNETIC STIMULATION
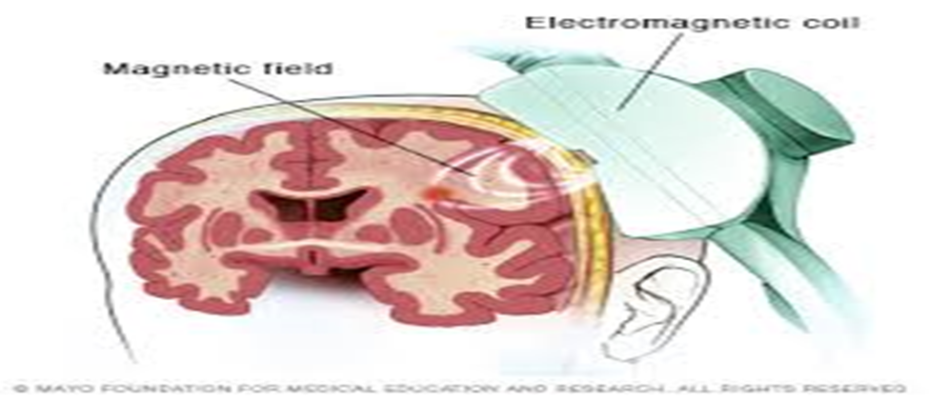
TRANSCRANIAL MAGNETIC STIMULATION
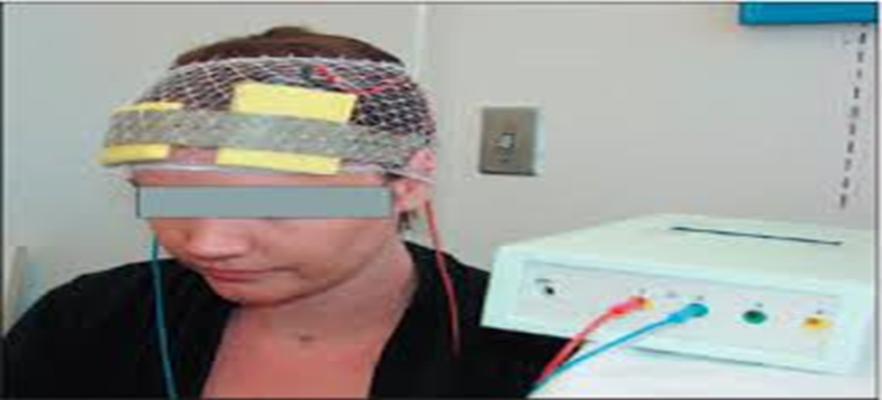
TRANSCRANIAL DIRECT CURRENT STIMULATION
Computers in speech therapy
- In rehabilitation department with as well as without speech therapist
- At home by interactive CDs and website
- Large expanding collection of practice material
- Multiple repetitions
Tele-therapy
- Video conferencing between single or multiple patients on one end and therapist on the other.
COMPUTERS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
- Smart phones
- Tablets
- Apps
- Interactive -software’s
- Tele-assessment
- Online and Offline accessibility
- Automated recorded,
- Storage
- Retrieval
- Analysis
- Comparison
- Scalability of number
- Variety of stimuli
- Experimental methods
- Voice to text
- Text to voice
- Image to text voice
- Machine translation
- Transliteration
- Cueing
- Follow up
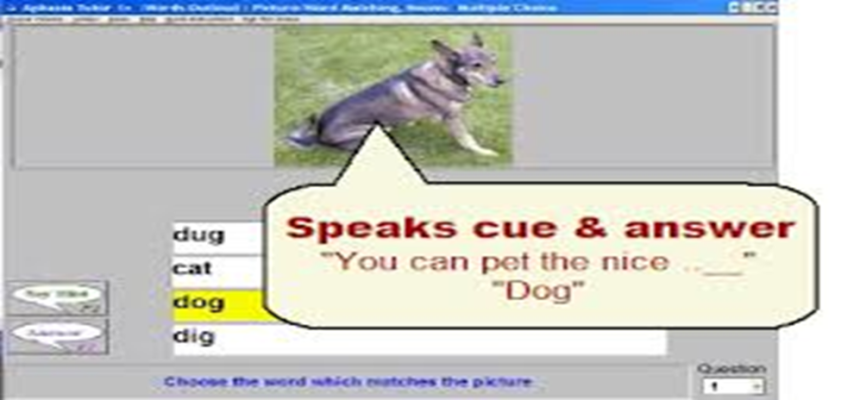
COMMERCIAL SOFTWARES ONLINE & OFFLINE

VIRTUAL SPEECH THERAPY
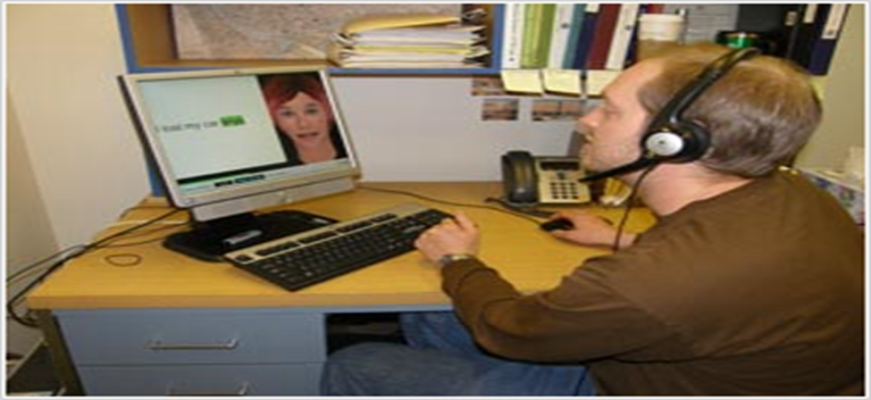

TELETHERAPY
TELETHERAPY
Social Phobia as a Result of Aphasia
Intense and recurring fear of one or more social situations in which the person in exposed to unknown people or potential assessment by others Persons with Aphasia should keep in contact with friends and participating in conversation on an equal basis.
They may have Problems with being exposed to a larger group of people.
Therapy:
Logopedic Treatment:
- Exercises for improving word recall and moderating stumbling speech,
- Preparing himself to speak in public
- Search for ways of assisting in speech problems and testing them in individual situations.
Psychological Treatment:
- Identification of negative automatic thoughts.
- Exposure therapy.
Social Approaches to Aphasia Rehabilitation
- Adopting a social model requires a philosophical shift from traditional, medical-model approaches.
- A Social model is based on the belief that communication is a social act; through communication we create and express our ideas, our identities, and our life values, and ensure our membership in society.
- In a social approach, communication and psychosocial functioning are considered inseparable.
- A social approach focuses not only on communication and life participation of those affected by aphasia, but also on the communicative, physical, social, and emotional environment.
- Long-term personal consequences of aphasia are the focus of intervention in a social approach.
- Traditional clinician roles and change with the adoption of social approaches.
- The ultimate aim of a social approach is to enhance the living of life with aphasia.
MANY ROLES OF CAREGIVERS
- As a good communication partner, with and without training.
- Need to assess burden, emotions, knowledge, attitude, practices
- As a person ‘speaking” for PWA
- As a link with clinician
- As an aid and assistant in therapy
- As a therapist herself
- As a participant in research
- As an advocate
- As a leader in Patient Support Groups
- As a narrative story teller

COMMUNICATION PARTNER TRAINING
Aphasia is indeed a family affair.
- Communication strategies and skills of aphasic speakers and their close ones can be augmented even after several years post stroke.
- Communication school can be a very essential alternative to individual speech therapy not only in the chronic phase but also in the acute phase of the rehabilitation plan about aphasia.
- The results showed that it is possible to increase the psychological well-being of aphasic persons and their close one by a well-planned communication school program.
- The educated volunteers will manage to aims of the communication school using the practice manual.
Advocacy Strategies for Supporting Participation of the Person with Aphasia
- Build public awareness and understanding of aphasia
- Establish attitudes and behaviors that promote inclusion
- Promote public knowledge of facilitating behaviors and accommodations.
- Provide communication aids and materials to support communication
- Provide communication in an accessible format (e.g., alternatives such as pictures and written instructions, multiple-modality communication, large print)
Advocacy Strategies for Supporting Participation of the Person with Aphasia
- Encourage environmental adaptations to promote communication (reduce noise, provide alerting systems, make speakers visible to the person with aphasia, alter signage)
- Alter information complexity
- Prepare for management of emergency or unexpected s.. (e.g., written message for transport driver, police, or staff)
- Provide accessible information regarding services.
Aphasia therapy with limited resources
- Group therapy
- Family members as therapist
- Physicians as therapists
- Computerized methods
- Tele-therapy
- Web-based self-practice tools
- The need to document current scenario about QOL for PWA in India
- Is there dearth of felt need for therapy & rehab. Amongst PWA, Caregivers and Therapists?
- How to improve the team approach for “Goal setting”?
- How to ensure reimbursement for expenses from medical insurance companies?
- How to impart “communication partner training” in group setting
- Need to assess and reduce caregiver burden.
- How to educate potential employers?
- Role of sheltered workshops
- Role of augmentative devices
- Role of occupation therapy in retraining
CONCLUDING REMARKS
1. Rehabilitation of people with aphasia and related disorders of speech and communication is a daunting imperative for society in general and various stakeholders in particular.
2. The burden at the levels of community, family and individual is large.
3. The problem is relatively neglected in comparison to many other ailments.
4. Evidence based behavioural and medical interventions are available, yet treatment gap is huge.
5 The nature of the challenge itself is difficult. There are problems in diagnosis, classification, and design of randomised controlled trials.
CONCLUDING REMARKS (2)
- Future progress will depend upon better theoretical understanding of neuroplasticity, standardised and validated objective and subjective assessments in multiple languages and cultures, multipronged team based intensive interventions and combinations of medical and social approaches.
- Short and long terms goals of rehabilitation should be SMART (Specific, Measurable, and Meaningful, Achievable, Realistic, and Time bound).
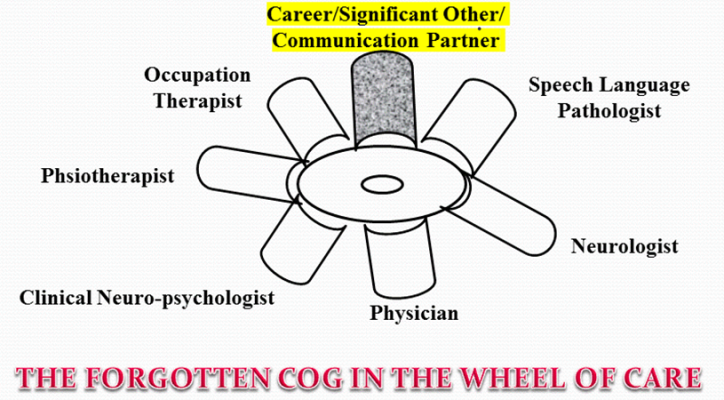
- An important but often forgotten cog in the wheel of care is caregiver or Significant Other’,
- Training of Communication Partners can go a long way in rehabilitation.
- When therapy and rehabilitation reach its limits, the clinicians become counsellors about acceptance, coping and optimum use of Augmentative and Assistive Devices.
- The future looks bright with strides in neurobiology and better leveraging of social factors through advocacy, awareness, and Life Participation Approach.
* * *





